A TensorFlow SavedModel may contain ReadFile and WriteFile operations, which may lead to data exfiltration and arbitrary file overwrite when the model is loaded.
The TensorFlow SavedModel format is a legacy format used by TensorFlow to store ML models. A SavedModel is a directory that contains a complete TensorFlow program, including weights and computation. It does not require the original model building code to run.
The SavedModel directory contains the TensorFlow program in a file called saved_model.pb, this is a ProtoBuf-serialized binary which contains the TensorFlow "computation graph".
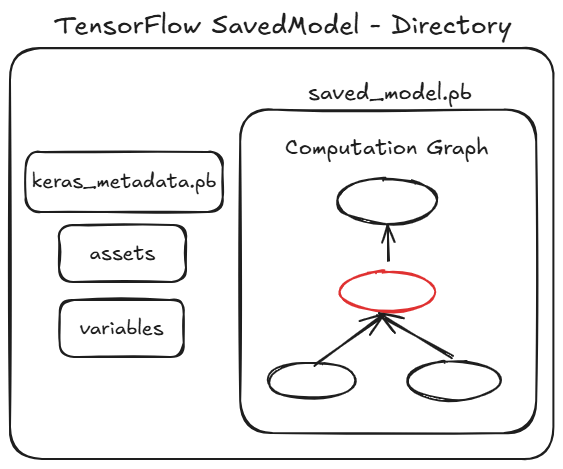
The computation graph specifies which operators to run on which variables.
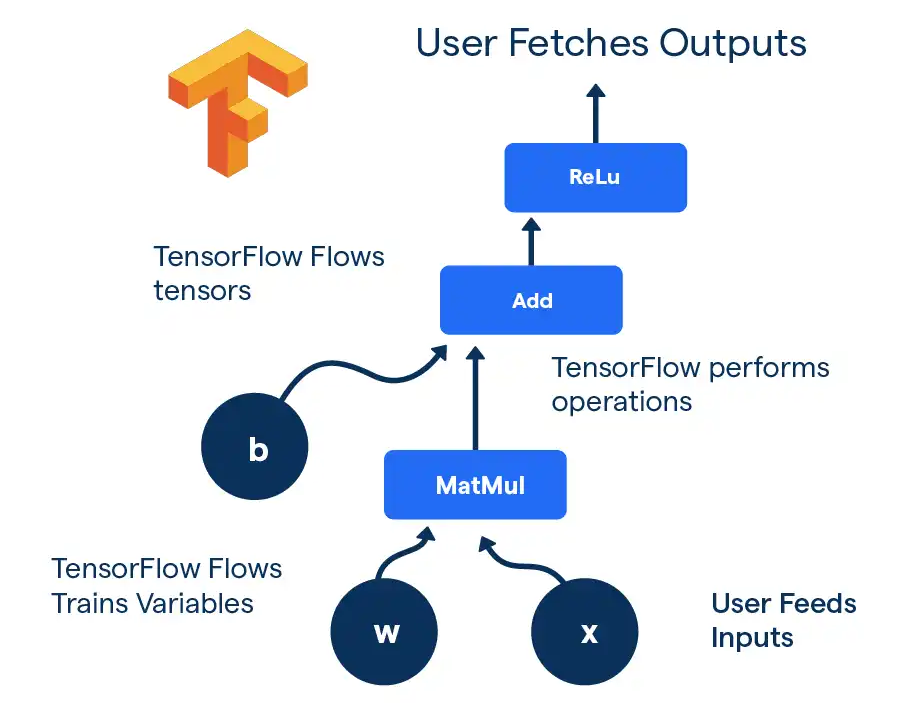
Two of the operators supported by TensorFlow are ReadFile and WriteFile, these operators are dangerous since they allow the model to interact with the underlying filesystem of the machine that loads the model.
For example, using ReadFile - a model would be able to read the machine's users file -
class MaliciousReader(tf.Module):
@tf.function
def __call__(self, input):
return tf.io.read_file("../../../../etc/passwd")
An even more severe example is a model that would rewrite a critical system file, such as SSH authorized_keys, allowing complete control of the machine by the attackers that injected their SSH key -
class MaliciousWriter(tf.Module):
@tf.function
def __call__(self, input):
data_to_write = tf.io.decode_base64("ZWNobyBwd25k")
tf.io.write_file("../../../../home/myuser/.ssh/authorized_keys", data_to_write)
return input + 2
Since the computation graph may include these malicious read/write operators, loading an untrusted TensorFlow SavedModel is considered to be dangerous.
[v] Model Load
[] Model Query
[] Other
To safely determine if the suspected TensorFlow SavedModel contains malicious code -
- Identify the
saved_model.pbfile in your SavedModel directory -
Load
saved_model.pband print anyReadFileandWriteFileoperators along with their inputs -import tensorflow as tf SAVEDMODEL_PATH = "/path/to/saved_model.pb" loaded_model = tf.saved_model.load(SAVEDMODEL_PATH) for func in loaded_model.signatures.values(): # Iterate over all operations in the graph for op in func.graph.get_operations(): if op.type == 'ReadFile' or op.type == 'WriteFile': args = [input_tensor.name for input_tensor in op.inputs] print(f"{op.name} {read_file_args}") - Examine the input filepaths to
ReadFileandWriteFileto determine whether these operations are malicious
Note that many legitimate ML libraries use ReadFile and WriteFile in a legitimate manner, therefore it is imperative to evaluate the arguments to these operators before deciding whether the model is malicious.
For example - many ML models use ReadFile with a user-supplied path (ex. arg0_0) in order to read input data for the model from the disk.
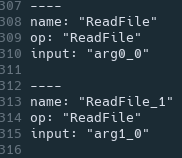
JFrog conducts extraction, decompilation and detailed analysis on each TensorFlow SavedModel, including evaluation of the arguments to ReadFile and WriteFile, in order to determine whether any malicious code is present.